Medicare Coverage
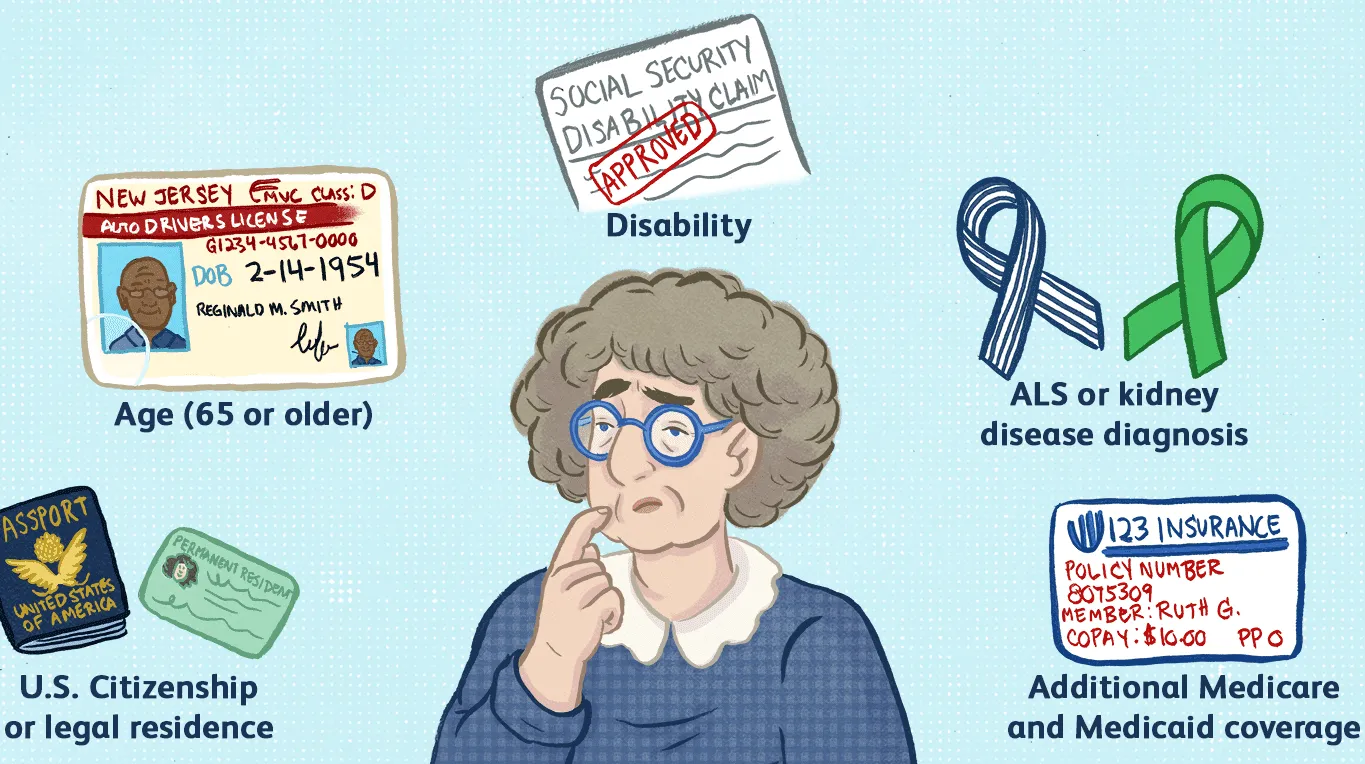
Medicare is a federally funded health insurance program that provides coverage to millions of Americans. It is primarily designed for people who are 65 years of age and older, but it also covers younger people with certain disabilities and conditions.
There are several different parts to Medicare coverage, each of which covers different services and treatments. Part A covers hospital stays, nursing care, and hospice care, while Part B covers medical services such as doctor's visits, lab tests, and preventive care. Part D covers prescription drugs, and Part C, also known as Medicare Advantage, allows beneficiaries to receive their Medicare benefits through private insurance plans.
One of the key benefits of Medicare is that it provides coverage for many services that are not covered by other insurance plans, such as long-term care and skilled nursing facilities. Additionally, Medicare often pays for a larger portion of medical costs than other insurance plans, which can be a significant financial relief for seniors.
However, it's important to note that Medicare does not cover everything. For example, it does not cover long-term care in the home, routine dental care, or most hearing aids. Many seniors choose to supplement their Medicare coverage with additional private insurance plans to cover these gaps.
In addition to the different parts of Medicare coverage, several different enrollment options exist. Most people are automatically enrolled in Medicare when they turn 65, but those who are not eligible for automatic enrollment can sign up during specific enrollment periods.
Overall, Medicare is an important source of health insurance for millions of Americans, and it provides a significant level of coverage for seniors and those with certain disabilities. While it may not cover everything, it can provide a valuable safety net for those in need of medical care.